The Brain Made Simple | The 4 Brain Regions & How They Work
You always feel like your body is an absolute marvel. It’s like a well-coordinated orchestra where every instrument plays its unique role. But guess who’s the maestro? Your brain! This extraordinary organ not only gathers and processes information but also keeps everything else in your body humming along smoothly. Now, imagine your brain as a committee of four brilliant experts, each with their own superpowers. While they do possess individual specialties, they collaborate seamlessly to optimize your mind, body, and spirit. So with this article delight on The Brain Made Simple let’s dive into this captivating world of the four brain regions. And, see how they bring about this extraordinary symphony.
What Are the Four Regions of the Brain | The Brain Made Simple
The brain is a complex and magnificent organ, composed of various parts working in perfect harmony. These are :
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Brain stem
Diencephalon
The Cerebrum | The Brain Made Simple
This is the superstar of the brain, occupying the largest space. It takes up the top part of the brain and accounts for 85% of its total volume.
Imagine the cerebrum as a spherical fruit, with its outermost layer ( The Grey Matter ! ) resembling a delicate, intricately patterned peel. This outer layer is called the cerebral cortex and is responsible for the remarkable cognitive processes that define our humanity.
While the cerebral cortex is the star of the show, the cerebrum has a hidden treasure trove beneath its surface, known as the subcortical structures ( The White Matter ). These structures are like the supporting actors, working tirelessly behind the scenes to ensure the smooth functioning of the cerebrum.
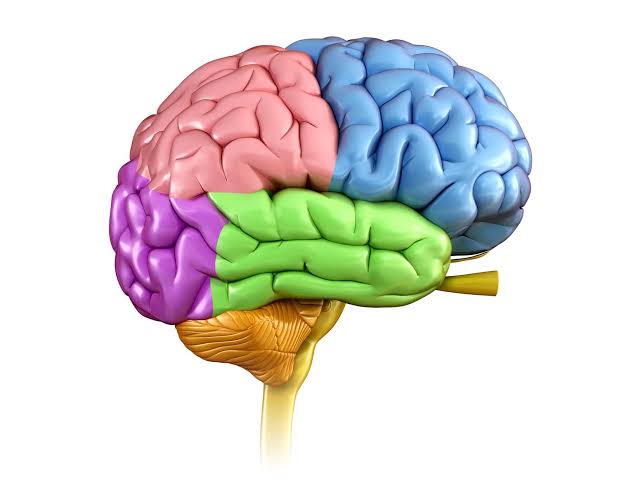
The cerebral cortex consists of two cerebral hemispheres, each split into four sections called lobes.Just like a bustling city, with four distinct districts !!
So, what are the lobes of the brain?

Here’s a short summary..
Parietal lobe
This middle part of the brain plays a crucial role in processing sensory information from the body, including touch, temperature, and pain. Additionally, the parietal lobe is responsible for spatial awareness, perception of objects, and coordination of movements.
Frontal lobe
Located at the front of the brain, the frontal lobe involves in your everyday planning and self-management. This includes emotional regulation, higher planning, and problem-solving. Additionally, it helps with body movement, memory consolidation, speech production, and word comprehension.
Temporal lobe
This part of the cerebral cortex is located at the sides of the brain. The function of the left temporal lobe is to manage sight and sound processing and the right, to control visual memory and language comprehension.
Occipital lobe
Located at the back part of the brain, the occipital lobe helps decode visual information — it processes the images it receives and sends them back to your eyes. It allows you to distinguish shapes as well as distances between the objects you see.
What does the cerebrum do?
Let’s say you experience a chill when you step out into the cold without a jacket or cry when watching a sad movie. That’s your cerebrum at work. It plays an important role in reasoning, learning, and feeling — both physical and emotional. Moreover, the cerebrum is also in charge of processing sensory information. Without it, you wouldn’t be able to hear or see.
The Cerebellum | The Brain Made Simple
Positioned under the back part of the cerebrum lies the cerebellum. This region of the brain is known as the “little brain” and takes up just 10% of the brain’s total volume. Similar to the cerebral cortex, you divide cerebellum into two hemispheres. The outer portion houses a network of neurons, while the inner part establishes communication with the cerebral cortex.
What does the cerebellum do?
The cerebellum, despite its small size, plays a crucial role in coordinating and fine-tuning our movements, maintaining balance, and assisting in certain cognitive functions. It acts as a skilled conductor, ensuring that our motor skills are executed smoothly and accurately. The cerebellum is involved in motor learning and the acquisition of new skills. It aids in the process of practicing and refining movements, allowing us to gradually improve our motor skills over time.
Although primarily associated with motor control, the cerebellum also has connections with cognitive functions. It contributes to certain aspects of attention, language processing, and working memory
The Brain Stem | The Brain Made Simple
The brainstem, a vital and often underappreciated part of the brain, serves as a bridge between the rest of the brain and the spinal cord. It is situated at the base of the brain, connecting the cerebrum, cerebellum, and spinal cord. It takes up about 4% of the brain’s total volume.
What does the brain stem do?
Although they make up a small percentage of the brain’s volume, you should be familiar with its three significant parts explained here..
The midbrain
Positioned at the top of the brainstem, the midbrain plays a crucial role in regulating eye movements. It contains specialized structures responsible for controlling the muscles that move the eyes, allowing us to track objects and shift our gaze.
The pon
The pons are located above the medulla oblongata majorly controls breathing as well as sleep regulation.
The medulla
Located at the bottom of the stem, it helps control your cardiovascular and respiratory systems. In addition, this part of the brain is also responsible for various reflexive actions. Every time you cough, sneeze, or vomit, it’s your body acting on the impulses sent from the medulla.
The Diencephalon | The Brain Made Simple
Smallest of the four brain sections. It’s tucked between the cerebrum and the brain stem and is, for the most part, hidden from view.
What does the diencephalon do?
Its first maestro is none other than the thalamus, the “gateway to the cortex.” This superstar structure receives sensory inputs from all corners of our body and like a diligent postman, redirects them to their rightful destinations in the cerebral cortex. Ensuring that we can appreciate the wonders of the world in all their glory.
But wait, there’s more! Enter the sensational sensation regulator – the hypothalamus. Positioned just below the thalamus, this celebrity is a master multitasker. The hypothalamus takes charge of maintaining equilibrium, like a diligent thermostat. It monitors body temperature and kicks into action when we need to cool down or warm up. But that’s not all – it also manages our primal needs and desires. Feeling famished? The hypothalamus can switch on the hunger alarm, prompting us to raid the fridge. Thirsty? It can signal our parched tongues to crave a refreshing sip. And when it comes to sleep and wakefulness, the hypothalamus takes the reins, ensuring we drift off into dreamland and wake up feeling refreshed.
Final Takeaway | The Brain Made Simple
And there you have it, a whirlwind tour of the brain’s four major regions! So, the next time you marvel at your ability to think, feel, or even tap your feet to a beat, remember that it’s all thanks to the intricate interplay of these four regions. All these brain regions work together like a well-oiled machine, passing messages to each other through fancy networks of brain cells. Understanding your brain regions and how they work is the first step to understanding how to optimize your mental well-being.
So, let’s keep exploring, learning, and spreading the word about the incredible wonders of our brain. It’s like having a personal superhero team inside our heads, and that’s something truly mind-boggling!
To understand your super brain even better do give this a watch https://youtu.be/g1is-3_c5LA
Read also : How to Calculate Your Metabolic Age | Metabolic Age vs. Chronological Age ( https://thebrightdelights.com/how-to-calculate-your-metabolic-age-metabolic-age-vs-chronological-age/ )